

1. Shri Visaolie Lhongu
ü State associated with - Nagaland
2. G20 Extraordinary Summit
ü G20 Extraordinary Leaders’ Summit will be organised to discuss the situation in Afghanistan.
ü This event will be convened by the G20 Italian Presidency in virtual mode.
ü During the meeting, top world leaders will discuss the response to humanitarian needs as well as access to basic services & livelihood in Afghanistan.
ü Leaders will also discuss the issues of counter terrorism, security and human rights.
ü G20 is an intergovernmental forum consisting of 19 countries and European Union (EU).
ü This grouping was founded in 1999 in the backdrop of several world economic crises. Since 2008, the group meets at least once a year.
3. UN Security Council Resolution 2593
ü Recently, the India-led United Nations Security Council (UNSC) adopted a Resolution 2593 on Taliban.
ü The resolution, sponsored by France, UK and the US, was adopted with 13 members, including India, voting in favour, none against it.
ü Two permanent and veto-wielding members Russia and China abstained.
ü The adoption of the resolution is a strong signal from the Security Council and the international community on its expectations in respect of Afghanistan.
ü It reiterates the importance of combating terrorism in Afghanistan, including those individuals and entities designated pursuant to resolution 1267 (1999)
ü It called for the Taliban to facilitate safe passage for people wanting to leave Afghanistan, allow humanitarians to access the country, uphold human rights, including for women and children and inclusive and negotiated political settlement.
4. IFFCO (Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited)
ü It is one of India's biggest cooperative societies which is wholly owned by Indian Cooperatives.
ü Founded in 1967 with just 57 cooperatives, today it is an amalgamation of over 36,000 Indian Cooperatives with diversified business interests ranging from General Insurance to Rural Telecom apart from its core business of manufacturing and selling fertilisers.
ü Objective: To enable Indian farmers to prosper through timely supply of reliable, high quality agricultural inputs and services in an environmentally sustainable manner and to undertake other activities to improve their welfare.
5. Rajmata Vijaya Raje Scindhia Ji
ü She was a prominent Indian political personality, known popularly as the Rajmata of Gwalior.
ü She was also an active member of the Jana Sangh and co-founder of Bharatiya Janata Party.
6. Extension of Swachh Bharat Mission till 2025-26
ü The Union Cabinet approved thecontinuation of Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban) till 2025-26, with focus on -
i. sustainability of Open Defecation Free (ODF) outcomes,
ii. achieving scientific processing of Solid Waste in all cities, and
iii. managing Wastewater in cities with less than 1 lakh population in Census 2011.
Fund sharing pattern between Centre and States:
ü Cities with million plus population: 25:75
ü Cities with population between 1-10 lakhs: 33:67
ü Cities with less than one lakh population: 50:50
ü Union territories without legislature: 100:0
ü Union territories with legislature: 80:20
7. Nutrition based subsidy for Phosphatic and Potassic Fertilizers
ü Under this Policy, the subsidy on Phosphatic and Potassic (P&K) fertilizers is announced by the Government on an annual basis for each nutrient on a per kg basis.
ü These rates are determined taking into account the international and domestic prices of P&K fertilizers, exchange rate, inventory level in the country etc.
ü NBS policy intends to increase the consumption of P&K fertilizers so that optimum balance (N:P:K= 4:2:1 ) of NPK fertilization is achieved.
ü This would improve soil health and as a result the yield from the crops would increase resulting in enhanced income to the farmers.
ü Also, as the government expects rational use of fertilizers, this would also ease off the burden of fertilizer subsidy.
ü It is being implemented from April 2010 by the Department of Fertilizers, Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers.
8. e-Sanjeevani Mission
ü eSanjeevani is the first-ever online OPD (outpatient) consultation service offered by the government of India to citizens.
ü The scheme was started in November 2019.
ü It is run by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
ü Also called the National Teleconsultation Service, it aims to provide healthcare services to patients in their homes.
ü It includes a structured and safe teleconsultation between a doctor and a patient through online mode (eSanjeevani OPD).
ü The eSanjeevani OPD portal and system has been developed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) in Mohali.
ü The panel of doctors on the service is drawn by the state governments.
ü The service is also available on mobile application.
9. e-PLI Bond
ü The Department of Posts has launched the digital version of the Postal Life Insurance policy bonds, also termed as “ePLI bond”.
ü The bond has been launched in collaboration with Digilocker.
ü All Postal Life Insurance subscribers would be able to download the digital copy of their policy bond from digilocker.
ü Both the Postal Life Insurance (PLI) and Rural Postal Life Insurance (RPLI) policy bonds are available in digital form.
ü It shall be treated at par with the original policy bond issued by the Department of Posts.
10. Negotiation from Gorkha representative from Darjeeling Hills, Terrai, Dooars, and the Government of West Bengal
ü MHA begins tripartite talks with Gorkhas, West Bengal government to resolve statehood demand in the North Bengal region.
ü Gorkhaland consists of Nepali-speaking people of Darjeeling, Kalimpong, Kurseong and other hilly districts of West-Bengal.
ü The people belonging to these areas have ethical, cultural and language differences with the Bengali community of West-Bengal.
ü The demand of Darjeeling as a separate administrative region dates back to 1907. But, the term “Gorkhaland” was coined recently, in the 1980s, by Subhash Ghising, the founder of Gorkha National Liberation Front (GNLF).
ü The Gorkhaland Movement is a movement mainly focused in the Darjeeling Hills of West Bengal, which demands the creation of a separate state of Gorkhaland.
ü The area covers Duars and Terai region of West Bengal.
11. AMRUT Mission till 2025-26
ü The Union Cabinet has approved the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation 2.0 (AMRUT 2.0) till 2025-26.
ü AMRUT was launched in 2015 to facilitate ease of living to citizens in 500 cities by providing tap connections and sewer connections.
ü AMRUT 2.0 focuses on:
i) Universal coverage of water supply by providing household tap connections in all 4,378 statutory towns.
ii) 100% coverage of household sewage/ septage management in 500 AMRUT cities
ü The mission will be monitored on a robust technology-based portal. The projects will be geotagged.
ü There will also be an endeavour to make it a paperless Mission.
ü The funds for the projects will be shared by the Centre, State and ULBs. Central funds will be released to the States in three tranches based on allocation to the State as per State Water Action Plan.
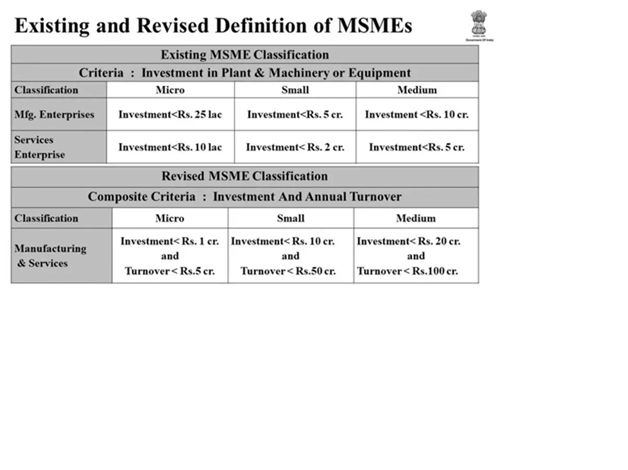
12. MSME Sector in India
ü Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006 which was notified on October 2, 2006, deals with the definition of MSMEs.
ü 6.3 crore MSMEs in India contribute one-third to the GDP of the country.
ü The sector is a critical source of livelihood and provides nearly 110 million jobs.
Note : Definition of MSME is in the above given image.
13. Maharatna status to Power Finance Corporation Ltd
ü An order to this effect was issued by the Department of Public Enterprises, under the Ministry of Finance.
ü PFC has become the 11th public sector enterprise to get the ‘Maharatna’ status in the country and joins the ranks of other such companies like ONGC, Indian Oil Corporation, Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL) and BHEL among others.
Maharatna” Status -
ü The Maharatna dispensation was ushered in by the Union government for mega Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) to become global giants (introduced in 2010).
ü “Maharatna” status is granted to a company which has recorded more than Rs. 5,000 crore of net profit for three consecutive years, an average annual turnover of Rs. 25,000 crore for three years or should have an average annual net worth of Rs. 15,000 crore for three years. It should also have global operations or footprints.
14. E-20 Fuel Program
ü E20 fuel is a blend of 20% of ethanol with gasoline.
ü Currently the permissible level of blending is 10% of Ethanol in India.
ü Ethanol is a biofuel. It is a common by product of biomass left by agricultural feedstock such as corn, sugarcane, hemp, potato, etc.
ü It will help in reducing emissions of carbon dioxide, hydrocarbons, etc.
ü It will help reduce the oil import bill, thereby saving foreign exchange and boosting energy security.
15. Kinds of Heavy Molasses
ü Molasses can be produced from citrus, wood sugar, sugar beet andsugarcane.
ü Different types are: integral or unclarified molasses, high-test molasses, A molasses, B molasses, C (final) molasses and syrup-off.
ü Integral high-test molasses is produced from unclarified sugarcane juice which has been partially inverted to prevent crystallization, then concentrated by evaporation until approximately 80% of DM content.
ü High-test molasses is basically the same as integral high-test molasses; however, since the sugarcane juice has been clarified before evaporation and therefore the impurities removed, the negative factors associated with integral high-test molasses are not present.
ü "A" molasses is an intermediate product obtained upon centrifuging the A masecuite in a raw sugar factory.
ü "B" molasses is also known as "second" molasses. It, too, is an intermediate product, obtained from boiling together "seed-sugar" and A molasses to obtain a B masecuite, which is then centrifuged to extract an additional 12% of raw sugar.
ü The last molasses is known as "C", "final" or "blackstrap" molasses and in some countries as "treacle". It is the end product obtained upon combining "virgin" sugar crystals obtained from syrup crystallization and B molasses to form a C masecuite, which after boiling and centrifuging produces C sugar and C molasses.
16. Index of Industrial Production
ü Index of Industrial Production data or IIP as it is commonly called is an index that tracks manufacturing activity in different sectors of an economy.
ü The IIP number measures the industrial production for the period under review, usually a month, as against the reference period.
ü IIP is a key economic indicator of the manufacturing sector of the economy.
ü There is a lag of six weeks in the publication of the IIP index data after the reference month ends.
ü IIP index is currently calculated using 2011-2012 as the base year.
ü The IIP data is compiled and published by CSO every month.
ü CSO or Central Statistical Organisation operates under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
17. Use Based Index
18. Consumer Price Index
ü It measures price changes from the perspective of a retail buyer.
ü It measures changes over time in the level of retail prices of selected goods and services on which consumers of a defined group spend their incomes.
ü Four types of CPI are as follows:
i. CPI for Industrial Workers (IW).
ii. CPI for Agricultural Labourer (AL).
iii. CPI for Rural Labourer (RL).
iv. CPI (Rural/Urban/Combined).
ü Of these, the first three are compiled by the Labour Bureau in the Ministry of Labour and Employment. Fourth is compiled by the Central Statistical Organisation (CSO) in the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
ü Base Year for CPI is 2012.
19. Food Price Index
ü It was introduced in 1996 as a public good to help in monitoring developments in the global agricultural commodity markets.
ü The FAO Food Price Index (FFPI) is a measure of the monthly change in international prices of a basket of food commodities.
ü It measures changes for a basket of cereals, oilseeds, dairy products, meat and sugar.
ü Base Period: 2014-16.
20. Handbook on Sustainable Management of Plastic Waster for Urban Local Bodies
ü The handbook provides a comprehensive overview to manage plastic waste by representing and discussing the components of entire plastic waste value chain.
ü It was launched with the motive of spreading awareness amongst the masses regarding the harmful effects of plastic.
ü Under the handbook, Urban local bodies (ULBs) are mandated to manage municipal solid waste & plastic waste, under the Municipal Solid Waste Management Rules 2016, and Plastic Waste Management Rules 2016, at the city level.
ü Handbook is a repository of 18 case studies or best practices from India, and 4 from south Asian countries.
ü The models outlined in this handbook aim to bring sustainable plastic waste management into practice. Several systems approach in this report are aligned with ‘Swachh Bharat Mission 2.0’ and ‘Plastic Waste Management Rules of 2016 & 2018’.
21. Competition Commission of India
ü Competition Commission of India (CCI) is a statutory body of the Government of India responsible for enforcing the Competition Act, 2002, it was duly constituted in March 2009.
ü The Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Act, 1969 (MRTP Act) was repealed and replaced by the Competition Act, 2002, on the recommendations of Raghavan committee.
ü Competition Commission of India aims to establish a robust competitive environment.
ü The Commission consists of one Chairperson and six Members as per the Competition Act who shall be appointed by the Central Government.
ü The commission is a quasi-judicial body which gives opinions to statutory authorities and also deals with other cases. The Chairperson and other Members shall be whole-time Members.